8 Types of Punctuation Marks
Learn the types of punctuation marks, which are like traffic lights for writing. From periods to commas, they help us organize our writing.

Learn the types of punctuation marks, which are like traffic lights for writing. From periods to commas, they help us organize our writing.
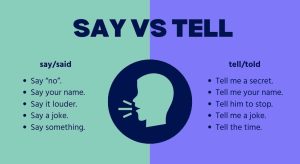
“Say” and “tell” are both verbs we use for communication. “Say” focuses on the words spoken. “Tell” needs someone to receive the info.

The present perfect tense form combines “have” or “has” with the past participle of a verb. It shows actions that are finished in the present.
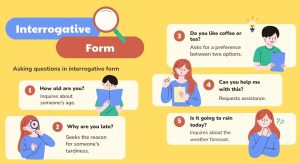
Interrogatives are the questions we ask to learn more. They help us learn about the world and gain new knowledge and connections.

This article will provide you some helpful tips on boosting your self-assurance so that you can speak English with confidence anytime.
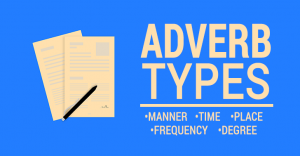
Adverbs can describe when (adverbs of time) or where (adverbs of place) something happens. Adverbs of manner express how something happens by simply adding -ly (in most cases).

For ESL students, English pronunciation is often difficult. This is why they can learn the sounds of English by first understanding the anatomy of the mouth

When you put two different words together, it forms another word and meaning. For example, compound words can have hyphens, spaces or no spaces at all between the two words.

For second language acquisition, there are five predictable stages. From preproduction to advanced fluency, it’s good to recognize the stage your students are in
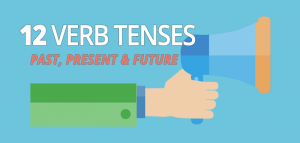
From the past, present and future, how well do you know your verb tenses? We list all 12 verb tense conjugation with examples using the verb “to travel”.