All 12 Verb Tenses in English – Past, Present and Future Verb Conjugation
All 12 Verb Tenses in English – Past, Present and Future Verbs
Do you want to improve your English verb tense skills? A good place to start is this list of all 12 verb tenses where we give the verb conjugation for the verb “to travel”.
From the past, present, and future, how well do you know your verb tenses?
For teachers, this article will help you brush up on your memory. Otherwise, if you’re a student, there are tons of examples to help you master verb conjugation.
Take a look at these 12 types of verb conjugation:
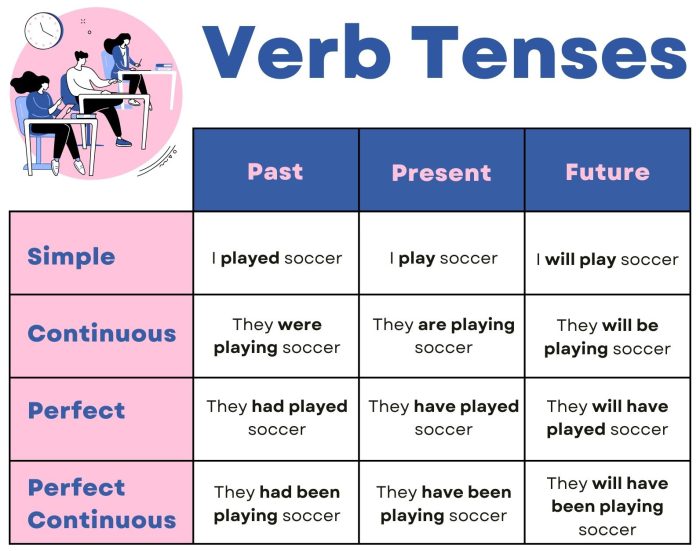
The 12 Verb Tenses in English
Before we begin, here’s a list of the 12 verb tenses in English:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous/Progressive
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous/Progressive
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous/Progressive
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous/Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect
- Future Continuous/Progressive
- Future Perfect Continuous/Progressive
Present Simple Verb Tense
When you use the present simple, you are using a routine. It’s something that you always do every day, month, or year. Or it’s something that you never do.
PRESENT VERB TENSE EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They: travel every day.
- He, She, It: travels every day.
Present Continuous/Progressive Verb Tense
When you use present continuous, you are referring to what is happening right now. Also, it can be an action that is not yet complete.
PRESENT CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE EXAMPLES:
- I: am traveling right now.
- You, We, They: are traveling right now.
- He, She, It: is traveling right now.
Present Perfect Verb Tense
Although it’s easy to confuse this verb tense with present simple, the main difference is that the action is complete for present perfect. In other words, you are looking at the result right now without any words referring to time.
PRESENT PERFECT EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They: have traveled to France.
- He, She, It: has traveled to France.
Present Perfect Continuous/Progressive Verb Tense
In this verb tense, the action starts in the past but it’s still continuing now. You have been performing the action and still are performing the action in the present.
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They: have been traveling for a day.
- He, She, It: has been traveling for a day.
Past Simple Verb Tense
For past simple, it includes a finished action and time.
PAST SIMPLE EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They, He, She, It: traveled to France yesterday.
Past Continuous/Progressive Verb Tense
When you use past continuous, you are often using two actions. However, one action is not finished in the past, and another completely interrupts the other action.
PAST CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE EXAMPLES:
- I, He, She, It: was traveling by bus when the deer crossed the road.
- You, We, They: were traveling when the deer crossed the road.
Past Perfect Verb Tense
This verb tense uses two actions at two different times. Before the second action occurs, the first action is complete.
PAST PERFECT EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They, He, She, It: had traveled by car when the bus arrived.
Past Perfect Continuous/Progressive Verb Tense
For colloquial English, we don’t use past perfect continuous very often. But in textbooks, it’s a bit more common. This very tense has a complete action that happened before a second action. But in this case, you can describe how long.
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They, He, She, It: had been traveling for one hour when the car broke down.
Future Simple Verb Tense
This verb tense is about planning things to do in the future. For example, what will you do tomorrow or next week?
Instead of using “will”, you can use “going to” for future tense. But this lesson uses “will” for the future tense.
FUTURE SIMPLE EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They, He, She, It: will travel to France tomorrow.
Future Continuous/Progressive Verb Tense
The action is not complete when another action happens in the future. This is similar to past continuous, but it refers to the future.
FUTURE CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They, He, She, It: will be traveling when you arrive.
Future Perfect Verb Tense
The action will be completed in the future before another is completed.
FUTURE PERFECT EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They, He, She, It: will have traveled to France by the time you arrive.
Future Perfect Continuous/Progressive Verb Tense
An action will be continuing in the future when it is interrupted by another action. This future verb tense often includes an indication of how long the action has been happening.
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE EXAMPLES:
- I, You, We, They, He, She, It: will have been traveling for one hour when you arrive.
Looking for verb activities?
We have a large set of ESL worksheets to help boost your verb conjugation and speaking skills. Here are some of our top verb worksheets:

Good
Why is the comment section filled with NPCs? lol
Thanks ever so much for developing these very good ideas, such is life-saving, the best thing that has happened is that I have found my reading room, please always be there to help me go through, for I need you always, with this platform I will be a good speaker
THANKS!
This helped me a lot, thank you very much
This information about verb tenses gave me new knowledge I learned. Thank you!
Very helpful.
thank you so much for this! very helpful.
Thank you so much. I’ve learned a lot.
Thanks, that was useful
You have opened my mind on tenses of verb.
Your work is appreciated
Thank you very much for answered my questions.
Thank you have got more knowledge about tenses,♨️
Ok nice thank you so much ….it is very usefull…..
Thank you very MUCH! Good work
I think you should have links to modal auxiliaries and to verb moods. It’s hard to feel a complete understanding of how verbs work without discussion of these two additional topics.
Thank you so much.
This was very helpful. Thank you for putting it all together.
Thank you so much ❤️
It was very easy to understand
The best thing is that it has all the tenses with example and their definition
Good details 👍
It was very helpful 😊 for me
It removed all my confusion regarding tenses
Last but not the least
THANK YOU 😊
Very much impressive!
Thank you very MUCH!
Thank you, I feel it’s more like Grammarly but complete.
I had been so restless for years to have this kind of explanation especially choosing the same sentence in all forms.
Thank you very much,
Qamar-uz-zaman
It’s really helped me to master my grammar.
Good details about tenses and it’s very useful for me
Amazing article. Very, very, very helpful in understanding English (as a born native speaker) and other languages.
This helped me a lot thank you 😊 🙏
This really help me improving my English grammar skills. Using these twelve tenses help me build my confidence in constructing a sentence even simple or complex. It can give me an idea about the correct uses of these words from past, present, future tenses and so on and to have a clear explanation regarding this matter.
Very informative and precise
Thanks very nice
So that very impressive post .
Thanks I got it!
Thank you people very much l have learned a lot from the all 12 tenses of verb
I was only informed by the six tenses but through my research I have gotten to know about all 12 tenses
Impressed 😊
Great work
Thanks a lot. But what about the present and past conditional tenses?
It is very easy to understand for beginners very useful as long as well.. expecting other tenses also like these method.👍
Thank you so much this is very useful for me
Very comprehensive. Thank you.
Very useful
It’s easy to understand and clarifies the confusion of tenses. Thank you.
A very good publication. Keep updating
Thanks, very useful guide!
Perfect job. Thank you…
Thanks alot for your nice Article 🥰🥰
Thank you.
Thank you got to know more about verbs 😊
It’s very useful for me
Perhaps this was answered already, but what tense is it when one says “The air is released from the tire… “? It’s a being verb in present tense used with the past participle released. There are a few other examples I have run across: is connected, are joined… Thank you.
Thank you very much. I have learned more about verb tenses.
Happy to discover the idea about English verb tenses with the help of examples and clearly stated explanation. Thank you so much.
You finally made this topic clear enough for me to fix it in my mind. Confidence in this topic allows me to paint with more subtle brushes. Time itself is so confusing and language just a translation…confidence in using all of the 12 forms opens many possibilities on paper.
Thanks so much.
Thanks you very much
Your article is very comprehensive.
Thanks so much. You really helped me understand fast especially with the examples.
Thank you very much. I have just learned in a minute. I am really happy
Thank you so much! The best explanation on the internet! I understood this in a minute!
Thank you so much
So easy, thank you so much.
Thank you so much for the details of verb tenses in English.
Simple to understand . Thank you so much ❤❤
It is very easy to understand.
Perfectly done!
It is very clear
Good explanation
Thank you so much for clearing up this concept…..😊😊
I don’t know what to say now, I come just to discover the site. I hope better and benefit for your next post, thanks!
I was really looking for this, thanks.
Thank you so much now I know better about verb tenses
Thanks man…
Thank you so much for this
Good work
It’s easy to learn and understand time and tense. Thanks a lot.
I have got your points, would you mind throwing light on Modular verbs?
Clear and concise explanations with suitable examples!
Thanks so much,this really help me on my GNS assignment 🥰🥰
Thanks
For more advanced learners, you might want to consider adding two more verb tenses. by separating out Future Simple we really have two: Spontaneous verb tense and Intentional (your Future Simple). Example, Person A: “I need the fire extinguisher!” Person B: “I’ll get it right now!” In a practical sense, Person B is currently doing the action, but it’s spontaneous, he wasn’t intending on getting it 5 minutes ago. The second verb tense would be hypothetical. “If I were rich.”
First there was darkness, and now there is light……what an excellent explanation ……thank you so much🙏
What a great explanation!!!
I thank you.
Thanks for your tremendous contribution
Simple and straightforward. 🙏🏽
It easy to learn and understand time and tense
Excellent explanation! I was very confused until I read this, makes much more sense now and definitely simplified it for me!
Thank you.
Missed the imperative…
Yes, because it’s not a tense. Imperatives are non-finite forms.
Thank you
Thanks so much very simple to understand
Your explanations are wonderful and very clear. However, I always thought that there ware 13 tenses. Where does “be going to tense” fit in? I am so confused now.
It’s another future time. There’s really no future “tense” in English, but we use different forms to indicate different aspects of the future action e.g. certainty, tentativeness, prediction etc. I think it does mention going to in one part.
Thank you!!! So simple!
I’m an ESL teacher and admittedly, identifying grammar/ structure is not my strong point. Can you please help me understand the structure/form/ tense of this sentence: What questions are you usually asked at an airport immigration counter?..Please help.Thank you.
Present perfect continuous tense.
It is a different version of the statement “I am usually asked this question at the airport counter.” Only that it is in question form! Think about it.
Even though I lived in UK nearly thirty years I have never gone to school to learn English so now decided to improve my English through internet. So, it’s very helpful and easy to learn. Thank you for your support.
Thank you very much, if I had had this explaining 40 years ago… It would have helped me so much!
Great to get those explanations now and be able to pass them on… 😉
You missed some passive tenses off:
Will Future Progressive
“Your hammer will be being mended…”
Future Perfect Progressive
“I will have been being driven”
Conditional Perfect Progressive:
“I would have been being driven mad by this infrequently used grammatical construction”
I have used these in everyday conversations and they roll of the tongue quite naturally.
It is extremely helpful to have all of the tenses together in one place. With expansion and examples.
I don’t have any materials. Now I have no objections.
Thank you so much for this
You removed my confusion 😊
Thank you so much for this! It’s my first year teaching ESL grammar, and while I have objectives, I don’t have any materials. It is extremely helpful to have all of the tenses together in one place, with explanations and examples.
Thanks I got it! Do you know in another website I couldn’t find every tense sometimes there are only tense with no examples. But this one is good.
Thanks for letting me know about the verb tenses and I needed to know much
Good details