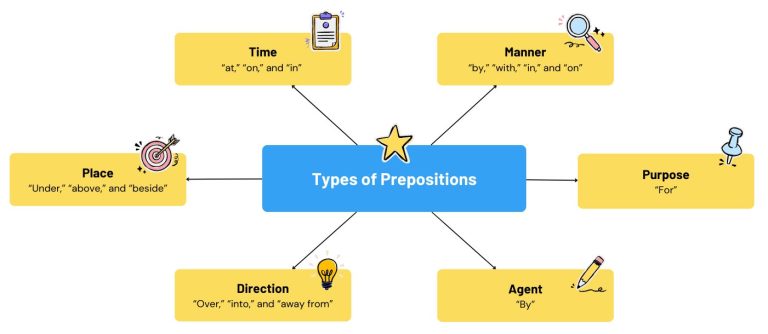
6 Types of Prepositions

The three main types of prepositions show location, time, or direction. For example, “in,” “at,” “on,” and “by” are common prepositions. But we sometimes also include purpose, manner, and agent as prepositions. More on that later.
1. Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time tell us when something happens. They include words like “at,” “on,” and “in.”
So, these words help us understand the timing of events. For example, “I’ll see you at noon” means the meeting time is exactly 12 o’clock during the day.
2. Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place show where something is located. “Under,” “above,” and “beside” are examples of prepositions of place.
Prepositions of place tell us where things are in relation to other things. By using these words, we can identify the locations of everything around us.
3. Prepositions of Direction
Prepositions of direction show the path something or someone moves along. They include words like “over,” “into,” and “away from”.
These types of prepositions show the movement of objects from one location to another. By using this type of preposition, we can understand the path that the objects or people take.
The 3 types of prepositions above are the most common. Below, you’ll find 3 other types of prepositions. Although they get less usage, we still use them as prepositions in the English language.
4. Prepositions of Agent
We use prepositions of agent in passive sentences with the word “by”. This type of preposition indicates the person or thing that performs the action of the verb.
Here’s an explanation of each one of these prepositions of agent.
- “The novel was written by George Orwell.”
- This sentence indicates that George Orwell is the person who wrote the novel.
- “The cake was baked by my mother.”
- Here, “by my mother” specifies who baked the cake.
- “The building was designed by the architect.”
- In this example, the architect is identified as the one who designed the building.
- “The mystery was solved by the detective.”
- This sentence tells us that the detective is the one who solved the mystery.
- “The song was sung by the choir.”
- This example shows that the choir is the group performing the action of singing the song.
While “by” is the most common preposition of agent, we can also use “with” or “through” in certain contexts. For example, we use “with” when referring to using tools like “She cut the paper with scissors.”
5. Prepositions of Purpose
Prepositions of purpose explain the purpose of an action. The most common preposition of purpose is “for”. But others can also provide this function depending on the context.
Here are five examples:
- “The room is used for meetings.”
- This sentence indicates that the purpose of using the room is to hold meetings.
- “He went to the store for some milk.”
- Here, “for some milk” explains the reason why he went to the store.
- “These shoes are great for running.”
- “For running” specifies the purpose of the shoes.
- “She saved money for her vacation.”
- In this example, “for her vacation” describes the purpose of saving money.
- “The fund was created for the benefit of the community.”
- “For the benefit of the community” explains the reason why the fund was created.
Prepositions of purpose clarify why actions are taken. They highlight intentions and reasons behind decisions and behaviors.
6. Prepositions of Manner
Prepositions of manner describe how something is done or the way in which it occurs. The most common prepositions of manner include “by,” “with,” “in,” and “on,” among others.
Here are five examples illustrating their use:
- “She answered the question with confidence.”
- “With confidence” describes the manner in which she answered the question.
- “The documentary was narrated by a voice actor.”
- “By a voice actor” specifies who narrated the documentary, indicating the manner or means by which the narration was performed.
- “They traveled to New York by train.”
- “By train” describes the mode of transportation used, indicating the manner of their travel.
- “The letter was written in ink.”
- “In ink” specifies the tool or medium used, indicating the manner in which the letter was written.
- “He speaks on behalf of the entire team.”
- “On behalf of” describes the manner or capacity in which he speaks, indicating he does so representing the team.
These examples show how prepositions of manner describe the method, means, or manner by which actions are performed.
Types of Prepositions
So, there you have it. We’ve provided you with the 6 types of prepositions – place, direction, agent, purpose, and manner.
They help us specify when, where, how, and why actions occur. And for the structure, they often come before nouns or pronouns.
Do you have any questions about the types of prepositions? We’d love to hear from you in the comment section below.