Adverbs of Frequency
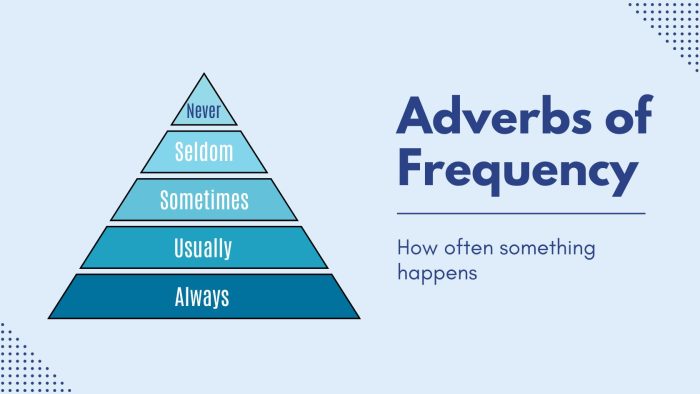
Adverbs of frequency tell us how often something happens. For example, words like “always,” “sometimes,” and “never” tell us how regularly actions occur. So, this type of adverb helps us understand if something is a daily habit or a rare event.
Examples of Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency are like our daily routines, telling us how often we do things. Let’s explore some common ones, each with its own unique frequency.
Here are some of the most common adverbs of frequency:
- Always (100%): This is a full-time commitment, happening without fail. If you always drink water first thing in the morning, it means you do it every single day, with no exceptions.
- Usually (80%): This one’s like a reliable friend who’s almost always there. If you usually take a walk after dinner, it means you do it most nights, but there might be a few exceptions.
- Often (60%): Often is when something happens more times than not. If you often read before bed, it means many nights find you with a book in your hand, but not always.
- Sometimes (40%): This is the halfway mark, where it’s hit or miss. If you sometimes skip breakfast, it means around half the time you do, and half the time you don’t.
- Rarely (20%): Here’s where things start to be uncommon. If you rarely eat out, it means dining at restaurants doesn’t happen often, making it a special occasion.
- Never (0%): Absolute zero, where an event just doesn’t happen. If you never drink coffee, it means you avoid it entirely, every single day.
Each of these adverbs adds a layer of meaning. It helps us share what we do and how often we do it.
Position of Frequency Adverbs
Let’s focus on where we place adverbs of frequency in sentences. Here are a couple of examples below.
Affirmative Adverbs of Frequency
“Vicky usually drives to work.” Here, “usually” is the adverb of frequency. We place it right before “drives,” which is the main action verb in the sentence. This is the common position for adverbs of frequency. It tells us how often the action happens.
“Vicky is never late for work.” In this sentence, “never” comes right after “is,” which is a form of the verb “to be.” This is where you put adverbs of frequency when using the verb “to be.” It shows how often the state or condition occurs.
Negative Adverbs of Frequency
“Vicky doesn’t usually walk.” This type of sentence places “usually” before the main verb “walk.” Even with “doesn’t” making the sentence negative, the adverb’s position doesn’t change. It still comes before the main action verb and tells us how frequently the action occurs.
“Vicky isn’t often late for work.” This sentence places “often” after “isn’t,” a negative form of the verb “to be.” This structure indicates how frequently a state or condition does not happen. The adverb’s position after the verb “to be,” even in a negative form, remains consistent with its placement in positive sentences.
Question Adverbs of Frequency
Does Vicky usually drive to work? In questions, the adverb of frequency often comes after the subject and before the main verb. So, “usually” is placed right after the subject “Vicky” and before the main verb “drive”.
Is Vicky sometimes late for work? The adverb of frequency “sometimes” comes after the auxiliary verb “is” and before the subject “Vicky”. This structure emphasizes the frequency of the situation.
The position of adverbs of frequency matters because they help the listener or reader understand exactly how often an action occurs.
List of Adverbs of Frequency
There are a lot of examples of adverbs of frequency so we’ve decided to list them out. We’ve also included a percentage and ordered them from the highest frequency.
| Adverb of Frequency | Percentage | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Always | 100% | Happens every time without fail. |
| Constantly | 90% | Happens continuously, almost always. |
| Habitually | 85% | Happens out of habit, very regularly. |
| Usually | 80% | Happens most of the time. |
| Frequently | 75% | Happens often, but not always. |
| Typically | 75% | Happens in a typical or expected way. |
| Often | 70% | Happens many times. |
| Generally | 70% | Happens in most situations. |
| Mostly | 65% | Happens the majority of the time. |
| Regularly | 60% | Happens at regular intervals. |
| Sometimes | 50% | Happens about half the time. |
| Periodically | 40% | Happens at specific intervals, not continuously. |
| Occasionally | 30% | Happens now and then, but not often. |
| Every now and then | 25% | Happens occasionally, but unpredictably. |
| Seldom | 20% | Rarely happens, but not never. |
| Infrequently | 15% | Rarely happens, less often than seldom. |
| Rarely | 10% | Hardly ever happens. |
| Hardly ever | 5% | Almost never occurs. |
| Almost never | 2% | Very rarely happens, close to never. |
| Never | 0% | Does not happen at all. |
Summary: Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency tell us how often something happens. They range from “always,” meaning all the time, to “never,” meaning not at all.
These words help us share our daily routines, special occasions, or things we avoid doing. They’re key for expressing our habits in our daily lives.
If you’re looking to teach adverbs of frequency, you can also take a look at our free adverb worksheets.
