Past Perfect Tense in English

Past Perfect Tense Form
The past perfect tense describes an action that happened before another action in the past. It’s formed by using “had” followed by the past participle of the verb.
For example, “She had finished her homework before dinner.” This sentence shows that finishing homework happens before eating dinner.
I want to start by showing you how the past perfect tense in a couple of different situations.
Regular Verbs Example
“They had walked to the store before it started raining.” It’s a regular verb because it ends with -ed.
Structure = Subject + had + past participle (regular verbs end in -ed)
Example = “They had walked to the park.”
This sentence shows that the action of walking to the store was completed before the rain began.
Irregular Verbs Example
“She had gone to bed early the night before the exam.” It’s an irregular verb because it doesn’t end with -ed.
Structure = Subject + had + past participle (irregular verbs do not end in -ed)
Example = “He had gone to the store.”
This sentence highlights that going to bed early was completed before the day of the exam arrived.
Negative Sentences Example
“She had not finished the project when the deadline arrived.” It becomes a negative sentence by adding “not”.
Structure = Subject + had + not + past participle)
Example = “She had not finished her project.”
This sentence indicates that the completion of the project did not occur before the deadline.
Question Form Example
“Had you ever visited Paris before last summer?” This question asks if the visit to Paris happened at some point before last summer.
Structure = Had + subject + past participle + ___?
Example = “Had they arrived before the meeting started?”
This simple structure helps you form sentences in the past perfect tense, whether they’re positive, negative, or questions.
Signal Words and Examples
Which words in English signal using the past perfect tense? It’s mostly words like “before,” “after,” “by the time,” “when,” and “until”.
Here are some quick examples:
- “He had left before I arrived.” This sentence shows that his leaving happened first.
- “After she had finished her homework, she watched TV.” Here, finishing homework comes before watching TV.
- “By the time we got to the station, the train had already departed.” This indicates the train’s departure happened first.
- “When they had completed the project, they felt relieved.” Completion precedes relief.
- “She had read the book until she fell asleep.” Reading happened up until falling asleep.
Each of these examples highlights how specific words cue the past perfect. They all clarify the sequence of events or conditions.

Past Perfect vs Simple Past
Mixing up the past perfect tense with the simple past is a common mistake. This happens a lot even for native speakers. I suggest to you to try not to complicate sentences.
Remember that the past perfect is for actions before another past event. For example, you use past perfect and simple past tenses like this:
- Past Perfect = “I had eaten before he arrived.”
- Simple Past = “I ate already.”
While simple past tense doesn’t imply another past action, past perfect does. Simple past is for actions that are already finished.
To correct these errors, check if there’s a clear sequence of events. If not, the simple past is likely your best choice. For instance, “I watched the movie and went to bed.” is grammatically correct.

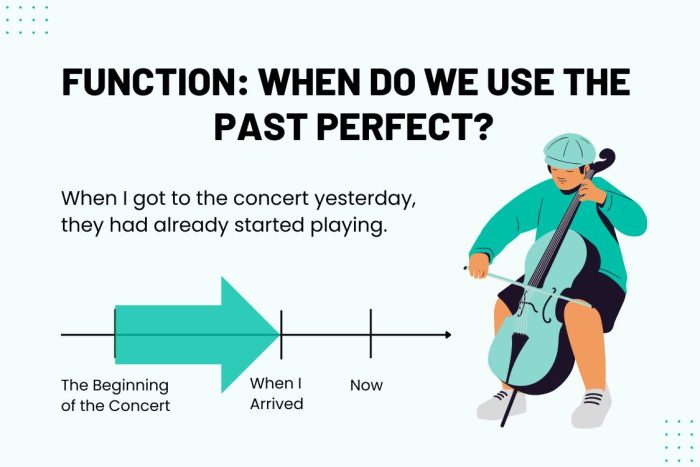
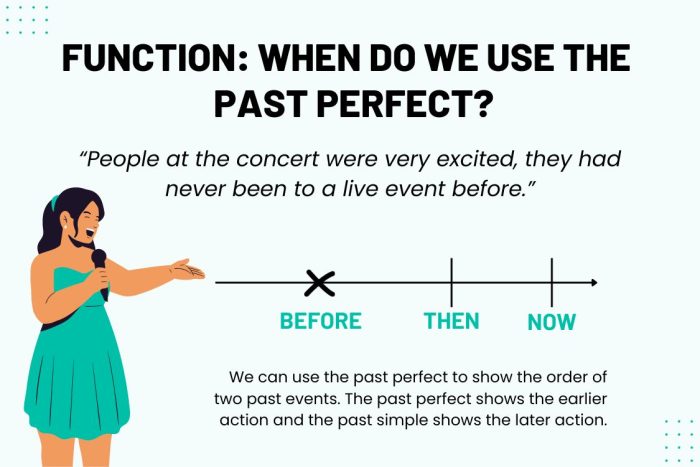
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
We use the past perfect tense to for actions completed before another past event. For example, “I had already eaten when she called.” This shows eating happened first. It’s also great for conditions not met in the past.
Here’s an example of this – “If you had told me, I would have helped.”
In this example, they didn’t know to help so this is why it didn’t happen. The past perfect tense helps us see the order of past events.
It also helps understand missed opportunities or unmet conditions. These examples show how we can use past perfect tense to better understand the chain of events in the past.
Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense gives us a unique way to talk about past actions and their sequences. By understanding how to use it, you can show when actions happened in the past.
Alright, that’s all I have for past perfect tense. Can you think of any examples of past perfect tense? We’d love to hear from you in the comment section below.
